Search This Blog
Hllo students hope u do'in good , welcome and search your query here
Featured Post
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
sound class 9 solutions NCERT CBSE
sound class 9 solutions NCERT CBSE
Question 1. What is sound and how is it produced?
Answer: Sound is mechanical energy that produces a sensation of hearing. When an object is set into vibrations, the sound is produced.
Question 3. Cite an experiment to show that sound needs a material medium for its propagation.
Answer: Take an electric circuit that consists of a cell, a switch, and an electric bell arranged inside a bell jar, which stands on the platform of an evacuating pump. The switch of the bell is pressed to close the electric circuit. When there is air within the bell jar, the sound is heard. Air is now pumped out of the bell jar. When the air is completely removed from the bell jar, no sound is heard as it is obvious from fig. because the medium of air that has to carry energy from the bell to the bell jar is removed. It shows that sound needs a material medium for its propagation.
Question 4. Why is a sound wave called a longitudinal wave?
Answer: Sound wave is called longitudinal wave because the particles of the medium vibrate in the direction of the propagation of the wave.
Question 5. Which characteristic of the sound helps you to identify your friend by his voice while sitting with others in a darkroom?
Answer: The characteristic of sound is quality or timbre.
Question 6. Flash and thunder are produced simultaneously. But thunder is heard a few seconds after the flash is seen, why?
Answer: The speed of sound is 330 m/sec in air medium at 0°C. Whereas the speed of light is 3 x 108m/sec. When we compare the speed of light with that of the speed of sound, the speed of light is greater than that of the speed of sound. Therefore thunder is heard a few seconds after the flash is seen.
Question 7. A person has a hearing range from 20 Hz to 20 kHz. What are the typical wavelengths of sound waves in air corresponding to these two frequencies? Take the speed of sound in air as 344 ms-1.
Answer:
Question 8. Two children are a± opposite ends of an aluminum rod. One strikes the end of the rod with a stone. Find the ratio of times taken by the sound wave in the air and in aluminum to reach the second child.
Answer:
Question 9. The frequency of a source/ sound is 100 Hz. How many times does it vibrate in a minute?
Answer:
Question 10. Does sound follow the same laws of reflection as light does? Explain.
Answer: Yes. Sound follows the same laws of reflection as that of light because,
(i) Angle of incidence of sound is always equal to that of the angle of reflection of sound waves.
(ii) The direction in which sound is incident, the direction in which it is reflected and normal all lie in the same plane.
Question 11. When a sound is reflected from a distant object, an echo is produced. Let the distance between the reflecting surface and the source of sound production remains the same. Do you hear echo sounds on a hotter day?
Answer: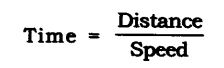
Time is inversely proportional to speed. As the temperature increases, the speed increases. Thus on a hot day due to high temperature the speed of sound increases. Hence the time will decrease and we can hear the echo sooner.
Question 12. Give two practical applications of reflection of sound waves.
Answer: Reflection of sound is used in megaphones, horns, and musical instruments such as trumpets and shehnai. It is used in a stethoscope for hearing a patient’s heartbeat. Ceilings of the concert halls are curved, so that sound after reflection reaches all comers of the hall. (Any two practical applications can be written).
Question 13. A stone dropped from the top of a tower 500 m high into a pond of water at the base of the tower. When is the splash heard at the top? Giving, g = 10 ms-2 and speed of sound = 340 m s-1.
Answer: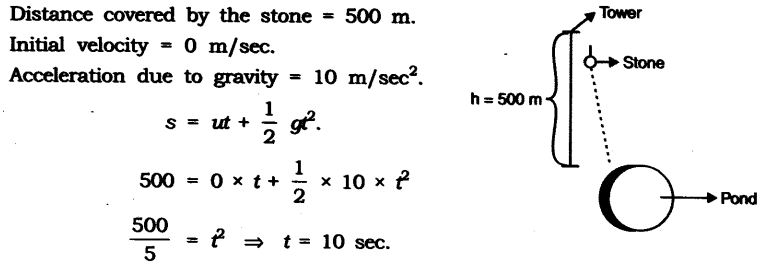
14. A sound wave travels at a speed of 339 ms-1. If its wavelength is 1.5 cm, what is the frequency of the wave? Will it be audible?
Answer:
Question 15. What is reverberation? How can it be reduced?
Answer: The persistence of sound in an auditorium is the result of repeated reflections of sound and is called reverberation.
To reduce the undesirable effects due to reverberation, roofs and walls of the auditorium are generally covered with sound-absorbent materials like compressed fiberboard, rough plaster, or draperies. The seat materials are also selected to have sound absorption properties.
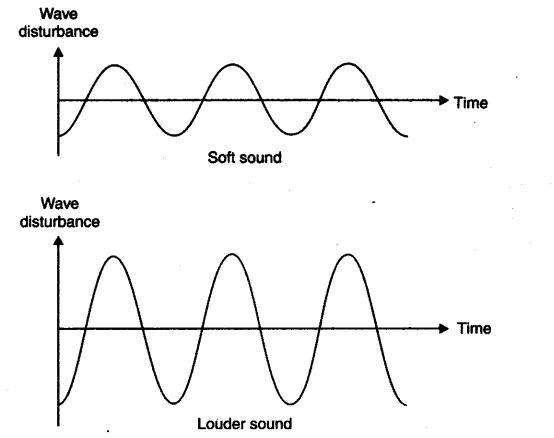
16. What is the loudness of sound? What factors does it depend on?
Answer: The loudness of sound is determined by its amplitude. The amplitude of the sound wave depends upon the force with which an object is made to vibrate. Loud sound can travel a larger distance as it is associated with higher energy. A sound wave spreads out from its source. As it moves away from the source its amplitude as well as its loudness decreases.
17. Explain how bats use ultrasound to catch prey.
Answer: Bats search out their prey by emitting and detecting reflections of ultrasonic waves. The high-pitched ultrasonic squeaks of the bat are reflected from the obstacles or prey and return to the bat’s ear. The nature of reflection tells the bat where the obstacle or prey is and what it is like.
Question 18. How is ultrasound used for cleaning?
Answer: Ultrasound is used to clean parts located in hard-to-reach places (i.e.) spiral tubes, odd-shaped parts, electronic components, etc. Objects to be cleaned are placed in a cleaning solution and ultrasonic waves are sent into the solution. Due to the high frequency, the dust particles, grease get detached and drop out. The objects thus get thoroughly cleaned.
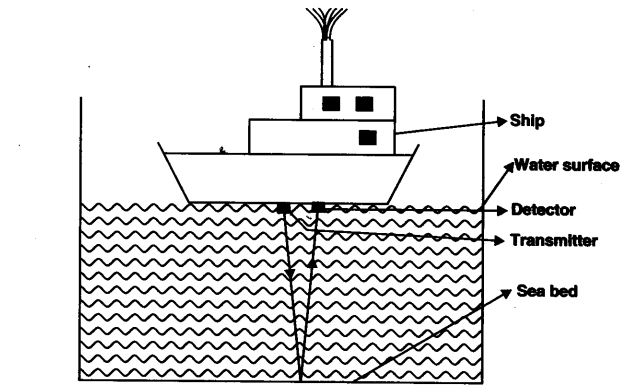
Question 19. Explain the working and application of a sonar.
Answer: Working: SONAR Consists of a transmitter and a detector and is installed in a boat or a ship as shown in fig. The transmitter produces and transmits ultrasonic waves. These waves travel through water and after striking the object on the seabed, get reflected back and are sensed by the detector. The detector converts the ultrasonic waves into electrical signals which are appropriately interpreted. The distance of the object that reflected the sound wave can be calculated by knowing the speed of sound in water and the time interval between the transmission and reception of the ultrasound.

Question 20. A sonar device on a submarine sends out a signal and receives an echo 5 s later. Calculate the speed of sound in water if the distance of the object from the submarine is 3625 m.
Answer: Time is taken between transmission and reception of signal = 5 sec.
Distance of the object from the submarine = 3625 m.
Question.21. Explain how defects in a metal block can be detected using ultrasound.
Answer. Ultrasounds can be used to detect cracks and flaws in metal blocks. Metallic components are used in the construction of big structures like buildings, bridges, machines, and scientific equipment. The cracks or holes inside the metal blocks, which are invisible from the outside reduces the strength of the structure. Ultrasonic waves are allowed to pass through the metallic block and detectors are used to detect the transmitted waves. If there is even a small defect, the ultrasound gets reflected back indicating the presence of the flaw or defect.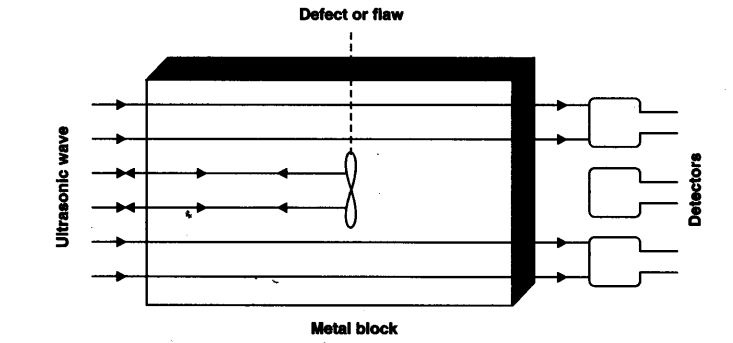
Question 22. Explain how the human ear works.
Answer: The outer ear is called “pinna. It collects the sound from the surroundings. The collected sound passes through the auditory canal. At the end of the auditory canal, there is a thin membrane called the eardrum or the tympanic membrane. When compression of the medium reaches the eardrum the pressure on the outside of the membrane increases and forces the eardrum inward. Similarly, the eardrum moves outward when a rarefaction reaches it. In this way, the eardrum vibrates. The vibrations are amplified several times by three bones (the hammer, anvil, and stirrup) in the middle ear. The middle ear transmits the amplified pressure variations received from the sound wave to the inner ear. In the inner ear, the pressure variations are turned into electrical signals by the cochlea. These electrical signals are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve and the brain interprets them as sound.
Popular Posts
Allen test series 2020 free pdf download for neet
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
the living world exemplar solutions NEET NCERT
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Allen Test Series For Neet 2017 Pdf Free Download
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
living world class 11th NCERT solutions CBSE
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
DC PANDEY for neet preparation pdf full book pdf
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
strategies for enhancement in food production solutions NCERT CBSE class 12
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Allen Test Series For Neet 2019 Pdf Free Download
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Allen Test Series For Neet 2018 Pdf Free Download
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
the fundamental unit of cell class 9 solutions NCERT CBSE
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps


Comments
Post a Comment
Hello ✋ welcome ,I hope u get something today