Search This Blog
Hllo students hope u do'in good , welcome and search your query here
Featured Post
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
electricity solutions class10 CBSE NCERT
electricity solutions class10 CBSE NCERT
1. A piece of wire of resistance R is cut into five equal parts. These parts are then
connected in parallel. If the equivalent resistance of this combination is R′, then the
ratio R/R′ is –
(a) 1/25 (b) 1/5 (c) 5 (d) 25
ans-(d)
2. Which of the following terms does not represent electrical power in a circuit?
(a) I
2R (b) IR2
(c) VI (d) V
2/R
ans-(b)
3. An electric bulb is rated 220 V and 100 W. When it is operated on 110 V, the
power consumed will be –
(a) 100 W (b) 75 W (c) 50 W (d) 25 W
ans-(d)
4. Two conducting wires of the same material and of equal lengths and equal diameters
are first connected in series and then parallel in a circuit across the same potential
difference. The ratio of heat produced in series and parallel combinations would be –
(a) 1:2 (b) 2:1 (c) 1:4 (d) 4:1
ans-(c)
5. How is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between
two points?
A voltmeter is connected in parallel to measure the potential difference between two points.
6. A copper wire has diameter 0.5 mm and resistivity of 1.6 × 10–8 Ω m. What will be
the length of this wire to make its resistance 10 Ω? How much does the resistance
change if the diameter is doubled?
Answer: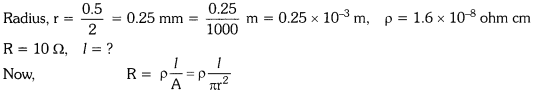
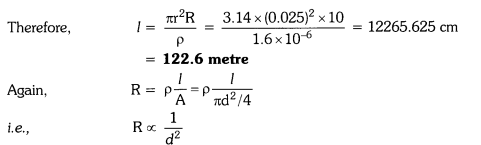
If a wire of diameter doubled to it is taken, then area of cross-section becomes four times.
New resistance =
Decrease in resistance = (10 – 2.5) Ω = 7.5 Ω
7. The values of current I flowing in a given resistor for the corresponding values of
potential difference V across the resistor are given below –
I (amperes) 0.5 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0
V (volts) 1.6 3.4 6.7 10.2 13.2
Plot a graph between V and I and calculate the resistance of that resistor.
ans- The graph between V and I for the above data is given below.
The slope of the graph will give the value of resistance.
Let us consider two points P and Q on the graph.
and from P along Y-axis, which meet at point R.
Now, QR = 10.2V – 34V = 6.8V
And PR = 3 – 1 = 2 ampere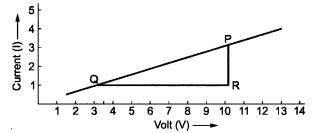
![]()
Thus, resistance, R = 3.4 Ω
8. When a 12 V battery is connected across an unknown resistor, there is a current
of 2.5 mA in the circuit. Find the value of the resistance of the resistor.
Here, V = 12 V and I = 2.5 mA = 2.5 x 10-3 A
∴ Resistance, R =
9. A battery of 9 V is connected in series with resistors of 0.2 Ω, 0.3 Ω, 0.4 Ω , 0.5 Ω
and 12 Ω, respectively. How much current would flow through the 12 Ω resistor?
Total resistance, R = 0.2 Ω + 0.3 Ω + 0.4 Ω + 0.5 Ω + 12 Ω – 13.4 Ω
Potential difference, V = 9 V
Current through the series circuit, I =
∵ There is no division of current in series. Therefore current through 12 Ω resistor = 0.67 A.
10. How many 176 Ω resistors (in parallel) are required to carry 5 A on a 220 V line?
suppose n resistors of 176 Ω are connected in parallel.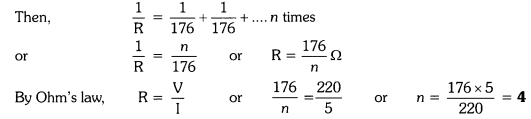
Thus 4 resistors are needed to be connected.
11. Show how you would connect three resistors, each of resistance 6 Ω, so that the
combination has a resistance of (i) 9 Ω, (ii) 4 Ω.
ans- Here, R1 = R2 = R3 = 6 Ω.
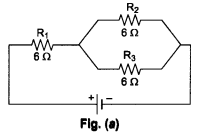
(i) When we connect R1 in series with the parallel combination of R2 and R3 as shown in Fig. (a).
The equivalent resistance is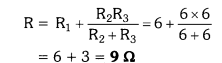
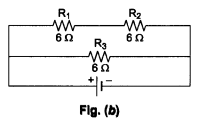
(ii) When we connect a series combination of R1 and R2 in parallel with R3, as shown in Fig. (b), the equivalent resistance is![]()
12. Several electric bulbs designed to be used on a 220 V electric supply line, are
rated 10 W. How many lamps can be connected in parallel with each other across
the two wires of 220 V line if the maximum allowable current is 5 A?
ans- Here, current, I = 5 A, voltage, V = 220 V
∴ Maxium power, P = I x V = 5 x 220 = 1100W
Required no. of lamps
∴ 110 lamps can be connected in parallel.
13. A hot plate of an electric oven connected to a 220 V line has two resistance coils
A and B, each of 24 Ω resistance, which may be used separately, in series, or in
parallel. What are the currents in the three cases?
(i) When the two coils A and B are used separately. R = 24 Ω, V = 220 V![]()
(ii) When the two coils are connected in series,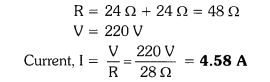
(iii) When the two coils are connected in parallel.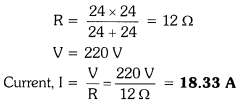
14. Compare the power used in the 2 Ω resistor in each of the following circuits:
(i) a 6 V battery in series with 1 Ω and 2 Ω resistors, and (ii) a 4 V battery in parallel
with 12 Ω and 2 Ω resistors.
(i) The circuit diagram is shown in figure.
Total resistance, R = 1Ω + 2Ω = 3Ω
Potential difference, V = 6 V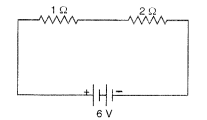
Power used in 2Ω resistor = I2R = (2)2 x 2 = 8 W
(ii) The circuit diagram for this case is shown :
Power used in 2 resistor = 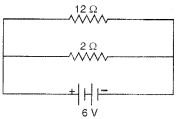
[ ∵ Current is different for different resistors in parallel combination.]
15. Two lamps, one rated 100 W at 220 V, and the other 60 W at 220 V, are connected
in parallel to electric mains supply. What current is drawn from the line if the supply
voltage is 220 V?
Power of first lamp (P1) = 100 W
Potential difference (V) = 220 V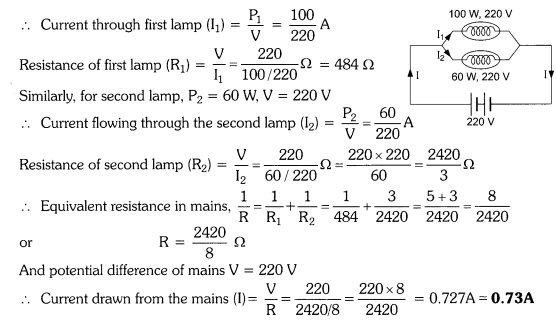
16. Which uses more energy, a 250 W TV set in 1 hr, or a 1200 W toaster in 10 minutes?
Energy used by 250 W TV set in 1 hour = 250 W x 1 h = 250 Wh
Energy used by 1200 W toaster in 10 minutes = 1200 W x 10 min
= 1200 x
Thus, the TV set uses more energy than the toaster.
17. An electric heater of resistance 8 Ω draws 15 A from the service mains 2 hours.
Calculate the rate at which heat is developed in the heater.
Here, R = 8 Ω, 1 = 15 A, t = 2 h
The rate at which heat is developed in the heater is equal to the power.
Therefore, P = I2 R = (15)2 x 8 = 1800 Js-1
18. Explain the following.
(a) Why is the tungsten used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamps?
(b) Why are the conductors of electric heating devices, such as bread-toasters
and electric irons, made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
(c) Why is the series arrangement not used for domestic circuits?
(d) How does the resistance of a wire vary with its area of cross-section?
(e) Why are copper and aluminium wires usually employed for electricity
transmission?
- The tungsten is used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamps because it has a very high melting point (3300°C). On passing electricity through tungsten filament, its temperature reaches to 2700°C and it gives heat and light energy without being melted.
- The conductors of electric heating devices such as bread-toasters and electric irons, are made of an alloy rather than a pure metal because the resistivity of an alloy is much higher than that of pure metal and an alloy does not undergo oxidation (or burn) easily even at high temperature.
- The series arrangement is not used for domestic circuits because in the series circuit, if one electrical appliance stops working due to some defect, than all other appliances also stop working because the whole circuit is broken.
- The resistance of a wire is inversely proportional to its area of cross-section, i.e., Resistance R ∝ (1/πr2). If the area of cross-section of a conductor of fixed length is increased, then resistance decreases because there are more free electrons for movement in the conductor.
- Copper and aluminum wires are usually employed for electricity transmission because they have very low resistances. So, they do not become too hot on passing electric current.
Popular Posts
Allen test series 2020 free pdf download for neet
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
the living world exemplar solutions NEET NCERT
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Allen Test Series For Neet 2017 Pdf Free Download
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
living world class 11th NCERT solutions CBSE
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
DC PANDEY for neet preparation pdf full book pdf
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
strategies for enhancement in food production solutions NCERT CBSE class 12
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Allen Test Series For Neet 2019 Pdf Free Download
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Allen Test Series For Neet 2018 Pdf Free Download
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
the fundamental unit of cell class 9 solutions NCERT CBSE
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Comments
Post a Comment
Hello ✋ welcome ,I hope u get something today