Search This Blog
Hllo students hope u do'in good , welcome and search your query here
Featured Post
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
carbon and its compounds class 10 solutions CBSE NCERT
carbon and its compounds class 10 solutions CBSE NCERT
1. Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6
has
(a) 6 covalent bonds.
(b) 7 covalent bonds.
(c) 8 covalent bonds.
(d) 9 covalent bonds.
ans-(b)
2. Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group
(a) carboxylic acid.
(b) aldehyde.
(c) ketone.
(d) alcohol.
ans-(c)
3. While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside,
it means that
(a) the food is not cooked completely.
(b) the fuel is not burning completely.
(c) the fuel is wet.
(d) the fuel is burning completely.
ans-(B)
4. Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
Covalent bond is formed by sharing of electrons so that the combining atoms complete their outermost shell.
In CH3Cl : C = 6, H = 1 and Cl = 17 And their electronic configuration is C – 2,4, H – 1 and Cl – 2, 8, 7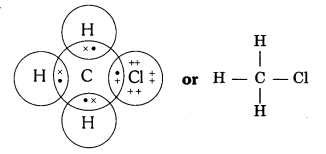
Three hydrogen atoms complete their shells by sharing three electrons (one electron each) of carbon atom.
Chlorine completes its outer shell by sharing its one out of seven electrons with one electron of carbon atom.
Thus carbon atom shares all its four electrons with three hydrogen atoms and one of chlorine atom and completes its outermost shell and single covalent bonds are formed in CH3Cl.
5. Draw the electron dot structures for
(a) ethanoic acid.
(b) H2S.
(c) propanone.
(d) F2 .
Answer: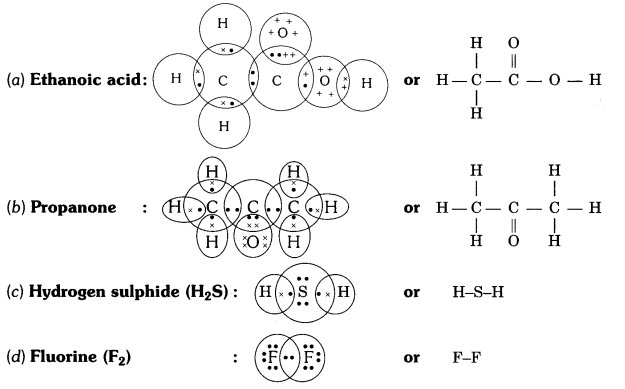
6. What is an homologous series? Explain with an example.
Homologous series : A homologous series is a group of organic compounds having
similar structures and similar chemical properties in which the successive compounds differ by -CH2 group.
Characteristics of homologous series :
(i) All members of a homologous series can be represented by the same general formula. For example, the general formula of the homologous series of alkanes is CnH2n+2, in which ‘n’ denotes number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in one molecule of alkane.
(ii) Any two adjacent homologues differ by one carbon atom and two hydrogen atoms in their molecular formulae.
(iii) The difference in the molecular masses of any two adjacent homologues is 14u.
(iv) All the compounds of a homologous series show similar chemical properties.
(v) The members of a homologous series show a gradual change in their physical properties with increase in molecular mass.
For example, general formula of the homologous series of alkanes is CnH2n+2, in which ‘n’ denotes number of carbon atoms in one molecule of alkane.
7. How can ethanol and ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical
and chemical properties?
| Property | Ethanol | Ethanoic acid |
| (i) State | Liquid | Liquid |
| (ii) Odour | Sweet smell | Pungent vinegar-like smell |
| (iii) Melting point | 156 K | 290 K |
| (iv) Boiling point | 351 K | 391 K |
Difference on the basis of chemical properties
| Test | Ethanol | Ethanoic acid |
| (i) Litmus test | No change in the colour of litmus solution. | Blue litmus solution turns red. |
| (ii) Sodium hydrogen carbonate test | C2H5OH + NaHCO3 → No reaction No brisk effervescence. | CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2 Brisk effervescence due to evolution of CO2. |
8. Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water? Will a micelle
be formed in other solvents such as ethanol also?
Micelle formation takes place when soap is added to water because the hydrocarbon chains of soap molecules are hydrophobic (water repelling) which are insoluble in water, but the ionic ends of soap molecules are hydrophilic (water attracting) and hence soluble in water.
Such micelle formation will not be possible in other solvents like ethanol in which sodium salt of fatty acids do not dissolve.
9. Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications?
Carbon and its compounds give a large amount of heat per unit weight and are therefore, used as fuels for most applications.
10. Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Hard water contains salts of calcium and magnesium. Calcium and magnesium on reacting with soap form insoluble precipitate called scum. The scum formation lessens the cleansing property of soaps in hard water.
11. What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red and blue)?
Red litmus will turn blue because soap is alkaline in nature. Blue litmus remains blue in soap solution.
12. What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
The addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated hydrocarbon to obtain a saturated hydro-carbon is called hydrogenation. The process of hydrogenation takes place in the presence of nickel (Ni) or palladium (Pd) metals as catalyst.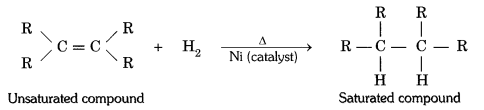
Application : The process of hydrogenation has an important industrial application. It is used to prepare vegetable ghee (or vanaspati ghee) from vegetable oils.
13. Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions:
C2H6 , C3H8 , C3H6 , C2H2 and CH4
ans- only in C3H6 and C2H2.
14. Give a test that can be used to differentiate between saturated and unsaturated
hydrocarbons.
Butter is a saturated carbon compound while cooking oil is an unsaturated carbon compound. An unsaturated compound decolourises bromine water, while a saturated compound cannot decolourise it. So we can distinguish chemically between a cooking oil and butter by the bromine water. Add bromine water to a little of cooking oil and butter taken in separate test-tubes.
- Cooking oil decolourises bromine water showing that it is an unsaturated compound.
- Butter does not decolourise bromine water showing that it is a saturated compound.
15. Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
When a dirty cloth is put in water containing dissolved soap, then the hydrocarbon end of the soap molecules in micelle attach to the oil or grease particles present on the surface of dirty cloth. In this way the soap micelle entraps the oily or greasy particles by using its hydrocarbon ends. The ionic ends of the soap molecules in the micelles, however, remain attached to water. When the dirty cloth is agitated in soap solution, the oily and greasy particles present on its surface and entrapped by soap micelles get dispersed in water due to which the soap water becomes dirty but the cloth gets cleaned. The cloth is cleaned thoroughly by rinsing in clean water a number of times.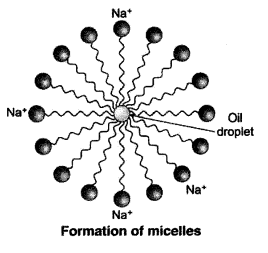
Popular Posts
Allen test series 2020 free pdf download for neet
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
the living world exemplar solutions NEET NCERT
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Allen Test Series For Neet 2017 Pdf Free Download
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
living world class 11th NCERT solutions CBSE
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
DC PANDEY for neet preparation pdf full book pdf
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
strategies for enhancement in food production solutions NCERT CBSE class 12
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Allen Test Series For Neet 2019 Pdf Free Download
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Allen Test Series For Neet 2018 Pdf Free Download
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
reproduction in organisms class 12 CBSE NCERT to the point
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Comments
Post a Comment
Hello ✋ welcome ,I hope u get something today